-
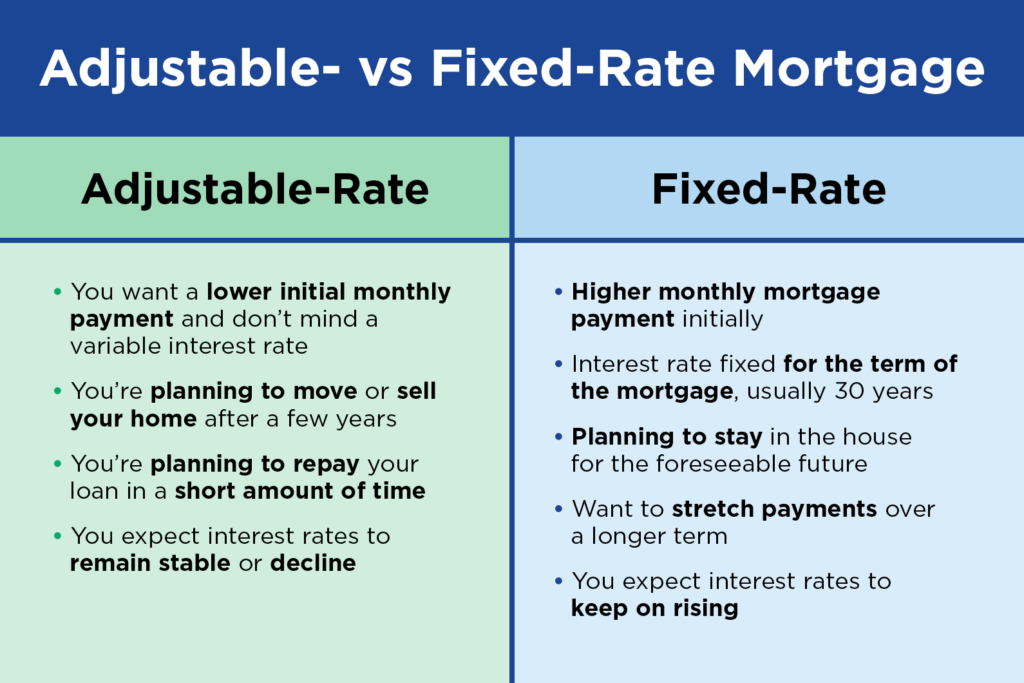
What types of mortgages are available? Common types include fixed-rate mortgages, adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs), FHA loans, VA loans, and jumbo loans. Each type has its own features and benefits.
- What is the difference between a fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgage? A fixed-rate mortgage has a consistent interest rate and monthly payment for the entire loan term. An adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) has an interest rate that can change periodically, typically after an initial fixed period.
-
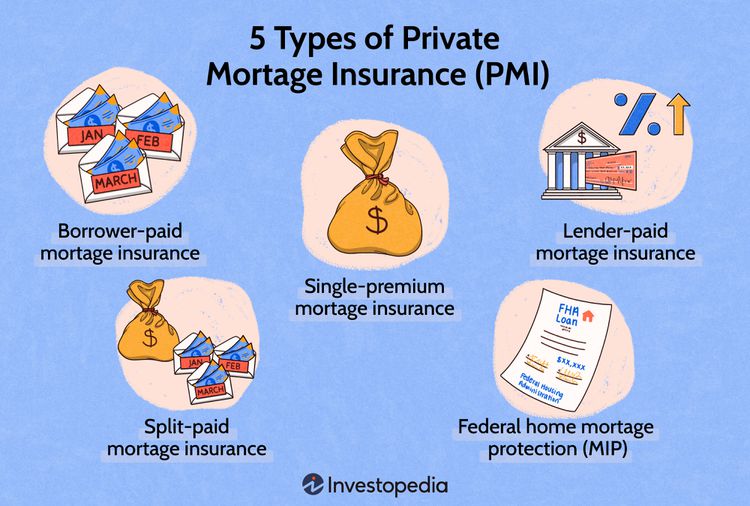
What is private mortgage insurance (PMI), and when is it required? PMI is insurance that protects the lender if the borrower defaults on the loan. It’s typically required for conventional loans with a down payment of less than 20%.
-
How much of a down payment do I need? Down payment requirements vary depending on the type of loan and lender. Conventional loans often require a down payment of 3% to 20% of the home’s purchase price, while FHA loans may require as little as 3.5%.
-
What factors affect my mortgage interest rate? Factors such as credit score, down payment amount, loan term, and current market conditions can influence your mortgage interest rate.
-
What is mortgage pre-approval, and why is it important? Mortgage pre-approval is a process where a lender evaluates your financial information to determine how much they’re willing to lend you for a home purchase. It’s important because it shows sellers that you’re a serious buyer and can afford the homes you’re interested in.
-
What documents do I need to apply for a mortgage? Common documents include pay stubs, W-2 forms, tax returns, bank statements, and proof of assets. Self-employed individuals may need to provide additional documentation.
-
Can I refinance my mortgage? Yes, refinancing involves replacing your current mortgage with a new one, often to take advantage of lower interest rates, change the loan term, or access equity in the home.
-
What happens if I miss a mortgage payment? Missing a mortgage payment can result in late fees, damage to your credit score, and eventually foreclosure if the issue isn’t resolved. It’s important to contact your lender immediately if you’re having trouble making payments.